Code Snippet Predict DL Experiments (python tutorial)
Decide Economic Index
Python Tutorial
Install xlrd
pip3 install xlrd
Read Excel
xl = pd.ExcelFile("dummydata.xlsx")
xl.sheet_names
>>[u'Sheet1', u'Sheet2', u'Sheet3']
df = xl.parse("Sheet1")
df.head()
parsed = pd.io.parsers.ExcelFile.parse(xl, "Sheet1")
parsed.columns
import pandas
df = pandas.read_excel(open('your_xls_xlsx_filename','rb'), sheetname='Sheet 1')
# or using sheet index starting 0
df = pandas.read_excel(open('your_xls_xlsx_filename','rb'), sheetname=2)
import pandas as pd
# open the file
xlsx = pd.ExcelFile(FileName.xlsx)
# get the first sheet as an object
sheet1 = xlsx.parse(0)
# get the first column as a list you can loop through
# where the is 0 in the code below change to the row or column number you want
column = sheet1.icol(0).real
# get the first row as a list you can loop through
row = sheet1.irow(0).real
import pandas as pd
# Read the excel sheet to pandas dataframe
DataFrame = pd.read_excel("FileName.xlsx", sheetname=0)
- read excel with specific row, column
import pandas as pd
# define the file name and "sheet name"
fn = 'Book1.xlsx'
sn = 'Sheet1'
data = pd.read_excel(fn, sheetname=sn, index_col=0, skiprows=1, header=0, skip_footer=1)
Transpose column
>>> d1 = {'col1': [1, 2], 'col2': [3, 4]}
>>> df1 = pd.DataFrame(data=d1)
>>> df1
col1 col2
0 1 3
1 2 4
>>> df1_transposed = df1.T # or df1.transpose()
>>> df1_transposed
0 1
col1 1 2
col2 3 4
Rename Column
>>> df = pd.DataFrame({'$a':[1,2], '$b': [10,20]})
>>> df.columns = ['a', 'b']
>>> df
a b
0 1 10
1 2 20
df.rename(columns={'pop':'population',
'lifeExp':'life_exp',
'gdpPercap':'gdp_per_cap'},
inplace=True)
Create DateTimeIndex in Pandas
import datetime as dt
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'year': [2015, 2016],
'month': [12, 1],
'day': [31, 1],
'hour': [23, 1]})
# returns datetime objects
df['Timestamp'] = df.apply(lambda row: dt.datetime(row.year, row.month, row.day, row.hour),
axis=1)
# converts to pandas timestamps if desired
df['Timestamp'] = pd.to_datetime(df.Timestamp)
>>> df
day hour month year Timestamp
0 31 23 12 2015 2015-12-31 23:00:00
1 1 1 1 2016 2016-01-01 01:00:00
# Create a DatetimeIndex and assign it to the dataframe.
df.index = pd.DatetimeIndex(df.Timestamp)
>>> df
day hour month year Timestamp
2015-12-31 23:00:00 31 23 12 2015 2015-12-31 23:00:00
2016-01-01 01:00:00 1 1 1 2016 2016-01-01 01:00:00
How to extract specific content in a pandas dataframe with a regex?
#convert column to string
df['movie_title'] = df['movie_title'].astype(str)
#but it remove numbers in names of movies too
df['titles'] = df['movie_title'].str.extract('([a-zA-Z ]+)', expand=False).str.strip()
df['titles1'] = df['movie_title'].str.split('(', 1).str[0].str.strip()
df['titles2'] = df['movie_title'].str.replace(r'\([^)]*\)', '').str.strip()
print df
movie_title titles titles1 titles2
0 Toy Story 2 (1995) Toy Story Toy Story 2 Toy Story 2
1 GoldenEye (1995) GoldenEye GoldenEye GoldenEye
2 Four Rooms (1995) Four Rooms Four Rooms Four Rooms
3 Get Shorty (1995) Get Shorty Get Shorty Get Shorty
4 Copycat (1995) Copycat Copycat Copycat
value = re.sub(r"[^0-9]+", "", value)
df['pricing'] = re.sub(r"[^0-9]+", "", df['pricing'])
df['Pricing'].replace(to_replace='[^0-9]+', value='',inplace==True,regex=True)
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(['$40,000*','$40000 conditions attached'], columns=['P'])
print(df)
# P
# 0 $40,000*
# 1 $40000 conditions attached
df['P'] = df['P'].str.replace(r'\D+', '').astype('int')
print(df)
#yields
P
0 40000
1 40000
Regular expression to extract numbers from a string
^ # start of string
\s* # optional whitespace
(\w+) # one or more alphanumeric characters, capture the match
\s* # optional whitespace
\( # a (
\s* # optional whitespace
(\d+) # a number, capture the match
\D+ # one or more non-digits
(\d+) # a number, capture the match
\D+ # one or more non-digits
\) # a )
\s* # optional whitespace
$ # end of string
[^0-9]+([0-9]+)[^0-9]+([0-9]+).+
Delete column from pandas DataFrame
del df['column_name']
Data Interpolation
from scipy import interpolate
from scipy.optimize import fsolve
import math
x = np.array([10,20,30,40,50])
y = np.array([0.2,0.6,-0.2,-0.5,0.7])
tck = interpolate.splrep(x, y, s=0)
xnew = np.arange(10,50,1)
ynew = interpolate.splev(xnew, tck, der=0)
# ynewder1 = interpolate.splev(xnew, tck, der=1)
# ynewder2 = interpolate.splev(xnew, tck, der=2)
plt.scatter(xnew,ynew)
How can I replace all the NaN values with Zero’s in a column of a pandas dataframe
df[1].fillna(0, inplace=True)
How to add an empty column to a dataframe?
df = pd.DataFrame({"A": [1,2,3], "B": [2,3,4]})
df
Out[18]:
A B
0 1 2
1 2 3
2 3 4
df.assign(C="",D=np.nan)
Out[21]:
A B C D
0 1 2 NaN
1 2 3 NaN
2 3 4 NaN
Pandas add one day to column
montdist['date'] + pd.DateOffset(1)
pd.DatetimeIndex(df.date) + pd.offsets.Hour(1)
mondist['shifted_date']=mondist.date + datetime.timedelta(days=1)
df['newdate'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date']).apply(pd.DateOffset(1))
df['newdate'] = pd.Series(index=df.index).tshift(periods=1, freq='D').index
covert pandas index to datetime index
import re
import datetime as dt
indexstrs = df_train.index
#indexstrs[0] = '2001-01-01'
years = [ int(re.sub(r'\D+','',rowstr.split('-')[0])) for rowstr in indexstrs]
months = [ int(re.sub(r'\D+','',rowstr.split('-')[1])) for rowstr in indexstrs]
days = [ int(re.sub(r'\D+','',rowstr.split('-')[2])) for rowstr in indexstrs]
indexnewstrs = [dt.datetime(years[i],months[i],days[i]) for i in range(len(years))]
#indexnewstrs
df_train['timeindex'] = indexnewstrs
df_train.index = pd.DatetimeIndex(indexnewstrs)
del df_train['timeindex']
df_train.head()
prevtpdate = df_train.index[0]
nexttpdate = df_train.index[0]
reward = 0
for curdate in df_train.index:
if curdate >= nexttpdate and prevtpdate < nexttpdate:
prevtpdate = nexttpdate
for _idx in df_turnpoints.index:
if curdate < _idx:
nexttpdate = _idx
# print("prevtpdate {} curdate {} nexttpdate {}".format(prevtpdate,curdate,nexttpdate))
break
curdatetostr = curdate.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
nexttptostr = nexttpdate.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
nextval = df_train[nexttptostr:nexttptostr]['Close'].values[0]
curval = df_train[curdatetostr:curdatetostr]['Close'].values[0]
reward = nextval - curval
print("reward {}".format(reward))
Pandas: Convert Timestamp to datetime.date
In [11]: t = pd.Timestamp('2013-12-25 00:00:00')
In [12]: t.date()
Out[12]: datetime.date(2013, 12, 25)
In [13]: t.date() == datetime.date(2013, 12, 25)
Out[13]: True
datetime to string with series in python pandas
date = dataframe.index #date is the datetime index
date = dates.strftime('%Y-%m-%d') #this will return you a numpy array, element is string.
dstr = date.tolist()
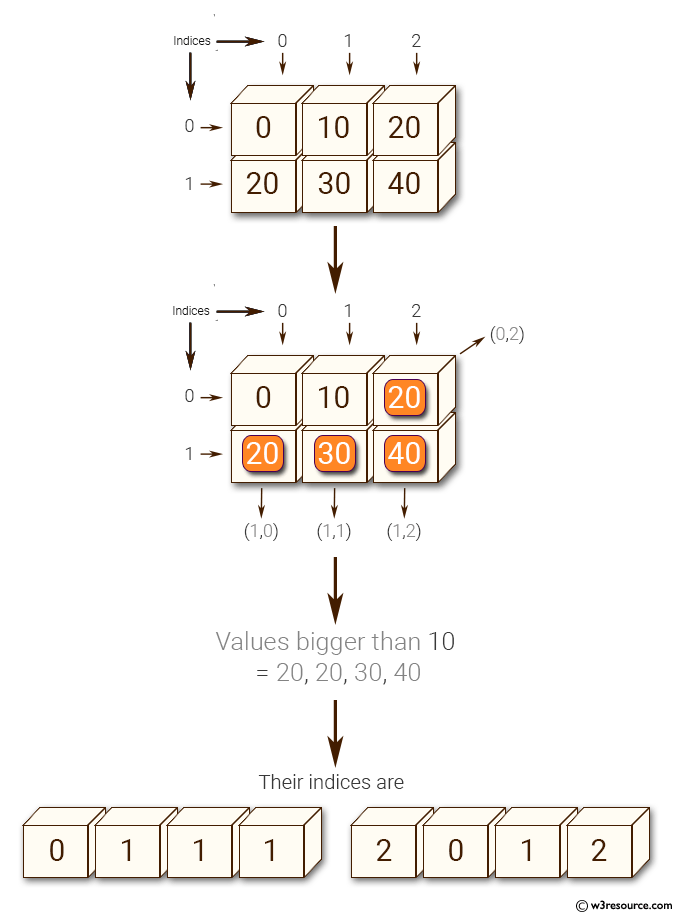
Python NumPy: Get the values and indices of the elements that are bigger than 10 in a given array
import numpy as np
x = np.array([[0, 10, 20], [20, 30, 40]])
print("Original array: ")
print(x)
print("Values bigger than 10 =", x[x>10])
print("Their indices are ", np.nonzero(x > 10))
Original array:
[[ 0 10 20]
[20 30 40]]
Values bigger than 10 = [20 20 30 40]
Their indices are (array([0, 1, 1, 1]), array([2, 0, 1, 2]))
add datetimeindex in the other datetime index
for i in range(data_preidxintrp.shape[0]):
basestr = data_preidxintrp.index[i]
basevalue = data_preidxintrp['value'][i]
if basestr not in dfkospinew.index:
while(True):
if basestr in dfkospinew.index:
basestr_timestamptostr = basestr.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
dfkospinew[basestr_timestamptostr:basestr_timestamptostr] = basevalue
break
basestr += pd.DateOffset(1)
xingdates = dfxing['날짜'].values
dates = pd.to_datetime(pd.Series(xingdates), format = '%Y%m%d')
dates.apply(lambda x: x.strftime('%Y-%m-%d'))
numpy.zeros() in Python
# Python Program illustrating
# numpy.zeros method
import numpy as geek
b = geek.zeros(2, dtype = int)
print("Matrix b : \n", b)
a = geek.zeros([2, 2], dtype = int)
print("\nMatrix a : \n", a)
c = geek.zeros([3, 3])
print("\nMatrix c : \n", c)
Find the B-spline representation of 1-D curve (Interpolation)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.interpolate import splev, splrep
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 10)
y = np.sin(x)
spl = splrep(x, y)
x2 = np.linspace(0, 10, 200)
y2 = splev(x2, spl)
plt.plot(x, y, 'o', x2, y2)
plt.show()
Deleting multiple columns based on column names in Pandas
Deleting multiple columns based on column names in Pandas
yourdf.drop(['columnheading1', 'columnheading2'], axis=1, inplace=True)
for col in df.columns:
if 'Unnamed' in col:
del df[col]
df.drop([col for col in df.columns if "Unnamed" in col], axis=1, inplace=True)
df.drop(df.columns[22:56], axis=1, inplace=True)
How to add column to numpy array
How to add column to numpy array
my_data = np.random.random((210,8)) #recfromcsv('LIAB.ST.csv', delimiter='\t')
new_col = my_data.sum(1)[...,None] # None keeps (n, 1) shape
new_col.shape
#(210,1)
all_data = np.append(my_data, new_col, 1)
all_data.shape
#(210,9)
all_data = np.hstack((my_data, new_col))
#or
all_data = np.concatenate((my_data, new_col), 1)
Numpy expand dims
>>> y = np.expand_dims(x, axis=0)
>>> y
array([[1, 2]])
>>> y.shape
(1, 2)
>>>
>>> y = np.expand_dims(x, axis=1) # Equivalent to x[:,np.newaxis]
>>> y
array([[1],
[2]])
>>> y.shape
(2, 1)
Keras: How to save model and continue training?
Keras: How to save model and continue training?
model.save('partly_trained.h5')
del model
load_model('partly_trained.h5')
filepath="LPT-{epoch:02d}-{loss:.4f}.h5"
checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(filepath, monitor='loss', verbose=1, save_best_only=True, mode='min')
callbacks_list = [checkpoint]
# fit the model
model.fit(x, y, epochs=60, batch_size=50, callbacks=callbacks_list)
try:
model.load_weights(path_checkpoint)
except Exception as error:
print("Error trying to load checkpoint.")
print(error)
self.saver = tf.train.Saver()
model_name = self.model_name + ".model"
self.saver.save(
self.sess,
os.path.join(self.model_logs_dir, model_name),
global_step=step
)
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(self.model_logs_dir)
if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path:
ckpt_name = os.path.basename(ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
self.saver.restore(self.sess, os.path.join(self.model_logs_dir, ckpt_name))
How to prevent tensorflow from allocating the totality of a GPU memory?
How to prevent tensorflow from allocating the totality of a GPU memory?
# Assume that you have 12GB of GPU memory and want to allocate ~4GB:
gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=0.333)
sess = tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options))
Build Multiple Layer LSTM network
"[p0,p1,p3][p4,p5,p6] => 2 num steps, 3 input size"
"[p7,p8,p9] => 3 output size"
self.inputs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.num_steps, self.input_size], name="inputs")
self.targets = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.input_size], name="targets")
def _create_one_cell():
lstm_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMCell(self.lstm_size, state_is_tuple=True)
lstm_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.DropoutWrapper(lstm_cell, output_keep_prob=self.keep_prob)
return lstm_cell
cell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell(
[_create_one_cell() for _ in range(self.num_layers)],
state_is_tuple=True
)
val, state_ = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, self.inputs_with_embed, dtype=tf.float32, scope="dynamic_rnn")
ws = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([self.lstm_size, self.input_size]), name="w")
bias = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[self.input_size]), name="b")
self.pred = tf.matmul(last, ws) + bias
Normalization seq data
seq = [np.array([520.95]), np.array([521.43]), np.array([558.02]), np.array([580.85]), np.array([586.65]), np.array([589.92])]
print('seq[0] {} seq[0][0] {}'.format(seq[0],seq[0][0]))
seq = [seq[0] / seq[0][0] - 1.0] + [
curr / seq[i][-1] - 1.0 for i, curr in enumerate(seq[1:])]
seq
>> seq[0] [520.95] seq[0][0] 520.95
Out[19]:
[array([0.]),
array([0.00092139]),
array([0.07017241]),
array([0.04091251]),
array([0.00998537]),
array([0.00557402])]
numpy arrary to list
>>> a = np.array([1, 2])
>>> a.tolist()
[1, 2]
>>> a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
>>> list(a)
[array([1, 2]), array([3, 4])]
>>> a.tolist()
[[1, 2], [3, 4]]
Show DataFrame as table in iPython Notebook
Show DataFrame as table in iPython Notebook
from IPython.display import display, HTML
# Assuming that dataframes df1 and df2 are already defined:
print "Dataframe 1:"
display(df1)
print "Dataframe 2:"
display(HTML(df2.to_html()))
Tensor manipulation
t = np.array([[1., 2., 3.], [4., 5., 6.], [7., 8., 9.], [10., 11., 12.]])
pp.pprint(t)
print(t.ndim) # rank
print(t.shape) # shape
t = tf.constant([1,2,3,4])
tf.shape(t).eval()
>>array([4], dtype=int32)
>>array([ 1.5, 3.5], dtype=float32)
matrix1 = tf.constant([[3., 3.]])
matrix2 = tf.constant([[2., 2.]])
(matrix1+matrix2).eval()
>>array([[ 5., 5.]], dtype=float32)
tf.random_normal([3]).eval()
>>array([ 2.20866942, -0.73225045, 0.33533147], dtype=float32)
x = [[1., 2.],
[3., 4.]]
tf.reduce_mean(x).eval()
>>2.5
tf.reduce_mean(x, axis=0).eval()
>>array([ 2., 3.], dtype=float32)
tf.reduce_mean(x, axis=1).eval()
>>array([ 1.5, 3.5], dtype=float32)
x = [[0, 1, 2],
[2, 1, 0]]
tf.argmax(x, axis=0).eval()
>>array([1, 0, 0])
tf.argmax(x, axis=1).eval()
>>array([2, 0])
t = np.array([[[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5]],
[[6, 7, 8],
[9, 10, 11]]])
t.shape
>>(2, 2, 3)
tf.squeeze([[0], [1], [2]]).eval()
>>array([0, 1, 2], dtype=int32)
tf.expand_dims([0, 1, 2], 1).eval()
>>array([[0],
[1],
[2]], dtype=int32)
tf.one_hot([[0], [1], [2], [0]], depth=3).eval()
>>array([[[ 1., 0., 0.]],
[[ 0., 1., 0.]],
[[ 0., 0., 1.]],
[[ 1., 0., 0.]]], dtype=float32)
tf.cast([1.8, 2.2, 3.3, 4.9], tf.int32).eval()
>>array([1, 2, 3, 4], dtype=int32)
x = [1, 4]
y = [2, 5]
z = [3, 6]
# Pack along first dim.
tf.stack([x, y, z]).eval()
>>array([[1, 4],
[2, 5],
[3, 6]], dtype=int32)
tf.stack([x, y, z], axis=1).eval()
>>array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]], dtype=int32)
Numpy squeeze
>>> x = np.array([[[0], [1], [2]]])
>>> x.shape
(1, 3, 1)
>>> np.squeeze(x).shape
(3,)
>>> np.squeeze(x, axis=0).shape
(3, 1)
>>> np.squeeze(x, axis=1).shape
Traceback (most recent call last):
...
ValueError: cannot select an axis to squeeze out which has size not equal to one
>>> np.squeeze(x, axis=2).shape
(1, 3)
import tensorflow as tf
a, b, c = 2, 3, 4
x = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([a, b, c], mean=0.0, stddev=1.0, dtype=tf.float32))
s = tf.shape(x)
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
v1, v2, v3 = sess.run(s)
y = tf.reshape(x, [v1 * v2, v3])
shape = tf.shape(y)
print (sess.run(y))
print (sess.run(shape))
a = tf.constant([[30, 29, 19, 17, 12, 11],
[30, 27, 20, 16, 5, 1],
[28, 25, 17, 14, 7, 2],
[28, 26, 21, 14, 6, 4]], dtype=tf.int32)
print(a.get_shape())
>>(4, 6)
a = tf.expand_dims(a, axis=2)
print(a.get_shape())
>>(4, 6, 1)
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
y_pred = sess.run([Y_pred], feed_dict={
X: trainX, Y: trainY})
print(y_pred[0].shape,type(y_pred))
new_y_pred = y_pred[0]
new_y_pred = tf.expand_dims(new_y_pred,axis=0)
print(new_y_pred.get_shape())
axis1 = new_y_pred.get_shape()[1]
print(int(int(axis1)/5))
axis1 = int(int(axis1)/5)
#new_y_pred = tf.reshape(new_y_pred,[])
new_y_pred = tf.reshape(new_y_pred,[axis1,5,1])
print(new_y_pred.get_shape())
>>(3005, 1) "<class 'list'>"
>>(1, 3005, 1)
>>601
>>(601, 5, 1)
matplotlib legend
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(days, truths, label='truth')
plt.plot(days, preds, label='pred')
plt.legend(loc='upper left', frameon=False)
plt.xlabel("day")
plt.ylabel("normalized price")
plt.ylim((min(truths), max(truths)))
plt.grid(ls='--')
plt.savefig(figname, format='png', bbox_inches='tight')#, transparent=True)
Adding new column to existing DataFrame in Python pandas
Adding new column to existing DataFrame in Python pandas
df1['e'] = pd.Series(np.random.randn(sLength), index=df1.index)
>>> df1.loc[:,'f'] = p.Series(np.random.randn(sLength), index=df1.index)
>>> df1
a b c d e f
6 -0.269221 -0.026476 0.997517 1.294385 1.757167 -0.050927
8 0.917438 0.847941 0.034235 -0.448948 2.228131 0.006109
>>>
df1 = df1.assign(e=p.Series(np.random.randn(sLength)).values)
numpy generating random sin curve
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
>>> x = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 201)
>>> plt.plot(x, np.sin(x))
>>> plt.xlabel('Angle [rad]')
>>> plt.ylabel('sin(x)')
>>> plt.axis('tight')
>>> plt.show()
calculate turning points / pivot points in trajectory (path)
calculate turning points / pivot points in trajectory (path)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.ndimage
def first_derivative(x) :
return x[2:] - x[0:-2]
def second_derivative(x) :
return x[2:] - 2 * x[1:-1] + x[:-2]
def curvature(x, y) :
x_1 = first_derivative(x)
x_2 = second_derivative(x)
y_1 = first_derivative(y)
y_2 = second_derivative(y)
return np.abs(x_1 * y_2 - y_1 * x_2) / np.sqrt((x_1**2 + y_1**2)**3)
def plot_turning_points(x, y, turning_points=10, smoothing_radius=3,
cluster_radius=10) :
if smoothing_radius :
weights = np.ones(2 * smoothing_radius + 1)
new_x = scipy.ndimage.convolve1d(x, weights, mode='constant', cval=0.0)
new_x = new_x[smoothing_radius:-smoothing_radius] / np.sum(weights)
new_y = scipy.ndimage.convolve1d(y, weights, mode='constant', cval=0.0)
new_y = new_y[smoothing_radius:-smoothing_radius] / np.sum(weights)
else :
new_x, new_y = x, y
k = curvature(new_x, new_y)
turn_point_idx = np.argsort(k)[::-1]
t_points = []
while len(t_points) < turning_points and len(turn_point_idx) > 0:
t_points += [turn_point_idx[0]]
idx = np.abs(turn_point_idx - turn_point_idx[0]) > cluster_radius
turn_point_idx = turn_point_idx[idx]
t_points = np.array(t_points)
t_points += smoothing_radius + 1
plt.plot(x,y, 'k-')
plt.plot(new_x, new_y, 'r-')
print('t_points {}'.format(t_points))
plt.plot(x[t_points], y[t_points], 'o')
plt.show()
#x, y = np.genfromtxt('bla.data')
y = np.array([0,2,3,4,5,2,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,7,6,5,4,5,6])
#x = np.arange(len(y))
x = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 50)
y = np.sin(x)*np.random.randint(10,size=1)
#print(x,y)
plot_turning_points(x, y, turning_points=20, smoothing_radius=1,cluster_radius=10)
The Ramer-Douglas-Peucker algorithm implemented in Python
The Ramer-Douglas-Peucker algorithm implemented in Python
Ramer–Douglas–Peucker algorithm
Ramer–Douglas–Peucker algorithm

numpy.asmatrix
>>> x = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
>>> m = np.asmatrix(x)
>>> x[0,0] = 5
>>> m
matrix([[5, 2],
[3, 4]])
numpy.hstack
>>> a = np.array((1,2,3))
>>> b = np.array((2,3,4))
>>> np.hstack((a,b))
array([1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 4])
>>> a = np.array([[1],[2],[3]])
>>> b = np.array([[2],[3],[4]])
>>> np.hstack((a,b))
array([[1, 2],
[2, 3],
[3, 4]])
tensorflow saver and restore
Zsaver = tf.train.Saver()
save_dir = 'checkpoints/'
if not os.path.exists(save_dir):
os.makedirs(save_dir)
save_path = os.path.join(save_dir, 'best_validation')
saver.save(sess=session, save_path=save_path)
saver.restore(sess=session, save_path=save_path)
tensorflow global step variable
tf.summary.scalar('loss',loss)
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate)
# Why 0 as the first parameter of the global_step tf.Variable?
global_step = tf.Variable(0, name='global_step',trainable=False)
train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss, global_step=global_step)
TensorFlow-Tutorials/10_save_restore_net.py
global_step = tf.Variable(0, name='global_step', trainable=False)
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(ckpt_dir)
if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path:
print(ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path) # restore all variables
start = global_step.eval() # get last global_step
print("Start from:", start)
"train "
global_step.assign(i).eval() # set and update(eval) global_step with index, i
saver.save(sess, ckpt_dir + "/model.ckpt", global_step=global_step)
Search A pandas Column For A Value
Search A pandas Column For A Value
df['preTestScore'].where(df['postTestScore'] > 50)
Selection and Indexing Methods for Pandas DataFrames
Selection and Indexing Methods for Pandas DataFrames
12 Useful Pandas Techniques in Python for Data Manipulation
12 Useful Pandas Techniques in Python for Data Manipulation
Pandas Cheat Sheet for Data Science in Python
Pandas Cheat Sheet for Data Science in Python
making matplotlib scatter plots from dataframes in Python’s pandas
making matplotlib scatter plots from dataframes in Python’s pandas
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
# df is a DataFrame: fetch col1 and col2
# and drop na rows if any of the columns are NA
mydata = df[["col1", "col2"]].dropna(how="any")
# Now plot with matplotlib
vals = mydata.values
plt.scatter(vals[:, 0], vals[:, 1])
mydata = df.dropna(how="any", subset=["col1", "col2"])
# plot a scatter of col1 by col2, with sizes according to col3
scatter(mydata(["col1", "col2"]), s=mydata["col3"])
Pandas Dataframe: Plot Examples with Matplotlib and Pyplot
Pandas Dataframe: Plot Examples with Matplotlib and Pyplot
scatter plot
buysignals = df_result['actions'].where(df_result['actions'] == 1)
sellsignals = df_result['actions'].where(df_result['actions'] == 0)
holdsignals = df_result['actions'].where(df_result['actions'] == 2)
df_result['buy'] = buysignals
df_result['sell'] = sellsignals
df_result['hold'] = holdsignals
df_result['buy'] = df_result['Close'].where(df_result['buy'] ==1)
df_result['sell'] = df_result['Close'].where(df_result['sell'] == 0)
df_result['hold'] = df_result['Close'].where(df_result['hold'] == 2)
df_result['datetime'] = df_result.index
import matplotlib, datetime
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def scatter_date(df, x, y, datetimeformat):
if not isinstance(y, list):
y = [y]
for yi in y:
plt.plot_date(df[x].apply(
lambda z: matplotlib.dates.date2num(
datetime.datetime.strptime(z, datetimeformat))), df[yi], label=yi)
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel(x)
# Example Usage
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
scatter_date(df_result, x='datetime', y=['Close','buy','sell','hold'], datetimeformat='%Y-%m-%d')
pandas access value by index number
In [28]: x = pd.DataFrame({'x': [1, 2, 3], 'y': [3, 4, 5]})
In [29]: x.iloc[1] = dict(x=9, y=99)
In [30]: x
Out[30]:
x y
0 1 3
1 9 99
2 3 5
pandas zero column creation and insert value
df_total['turnpoint'] = np.zeros(len(df_total))
df_total['turnpoint'].iloc[newx[1]] = newy[1]
df_total['turnpoint'].iloc[newx[1]]
Set value for particular cell in pandas DataFrame using index
Set value for particular cell in pandas DataFrame using index
df.loc[df[<some_column_name>] == <condition>, <another_column_name>] = <value_to_add>
df.loc[row_index,col_indexer] = value
df.iloc[[2], [0]] = 10
x = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6]})
x.iloc[1] = dict(A=10, B=-10)
Pandas sort
df = df.sort_values(['c1','c2'], ascending=[False,True])
pandas convert string to integer
s = lambda f: f.replace(',','')
dftotalname['A'] = dftotalname['A'].apply(s).astype(int)
pandas reset index
df = df.reset_index(drop=True)
How can I fill out a Python string with spaces?
How can I fill out a Python string with spaces?
print ('%06d'%123)
>> '000123'
'hi'.ljust(10)
>>'hi '
'{0: <6}'.format('Hi')
>>'Hi '
Read all files in the Directory
import glob
path = '/home/mypc/download/*.html'
files=glob.glob(path)
for file in files:
f=open(file, 'r')
print '%s' % f.readlines()
f.close()
Moving Average- Pandas
MovingAverage = pd.rolling_mean(Exchange,5)
df['MA'] = df.rolling(window=5).mean()
pandas df.pct_change()
df.pct_change()
In PANDAS, how to get the index of a known value?
In PANDAS, how to get the index of a known value?
In [48]: a
Out[48]:
c1 c2
0 0 1
1 2 3
2 4 5
3 6 7
4 8 9
In [49]: a.c1[a.c1 == 8].index.tolist()
Out[49]: [4]
In [25]: a.loc[a['c1'] == 8].index[0]
Out[25]: 4
In [17]: a.set_index('c1').index.get_loc(8)
Out[17]: 4
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
In [800]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(10).reshape(5,2),columns=['c1','c2'])
In [801]: df
Out[801]:
c1 c2
0 0 1
1 2 3
2 4 5
3 6 7
4 8 9
In [802]: np.where(df["c1"]==6)
Out[802]: (array([3]),)
In [803]: indices = list(np.where(df["c1"]==6)[0])
In [804]: df.iloc[indices]
Out[804]:
c1 c2
3 6 7
In [805]: df.iloc[indices].index
Out[805]: Int64Index([3], dtype='int64')
In [806]: df.iloc[indices].index.tolist()
Out[806]: [3]
matplotlib datetime plot
import matplotlib, datetime
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
datetimeformat='%Y-%m-%d'
x= [matplotlib.dates.date2num(datetime.datetime.strptime(idx.strftime('%Y-%m-%d'),datetimeformat)) for idx in _y.index]
y = dfstock['Close'][_y.index]
plt.plot_date(x,y)
Python : How to Merge / Join two or more lists
def main():
list1 = ["This" , "is", "a", "sample", "program"]
list2 = [10, 2, 45, 3, 5, 7, 8, 10]
print("list1 : ", list1)
print("list2 : ", list2)
finalList = list1 + list2
print("Merged List : " , finalList)
list1.extend(list2)
print("extended list1 : " , list1)
list1 = ["This" , "is", "a", "sample", "program"]
list2 = [10, 2, 45, 3, 5, 7, 8, 10]
list3 = [11, 12, 13]
finalList = list1 + list2 + list3
print("Merged List : " , finalList)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Pandas data copy
import copy
df_result =copy.deepcopy(df_test[SEQ_SIZE:])
PP print example
import pprint
pp = pprint.PrettyPrinter(indent=4)
pp.pprint(cm)
How to remove specific elements in a numpy array
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
index = [2, 3, 6]
new_a = np.delete(a, index)
print(new_a) #Prints `[1, 2, 5, 6, 8, 9]`
How To Concatenate Arrays in NumPy?
array2D_1 = array.reshape((3,3))
array2D_1
array([[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8]])
array2D_2 = np.arange(10,19).reshape(3,3)
array2D_2
array([[10, 11, 12],
[13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18]])
np.concatenate((array2D_1,array2D_2))
array([[ 0, 1, 2],
[ 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8],
[10, 11, 12],
[13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18]])
np.vstack((array2D_1, array2D_2))
array([[ 0, 1, 2],
[ 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8],
[10, 11, 12],
[13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18]])
np.hstack((array2D_1, array2D_2))
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 10, 11, 12],
[ 3, 4, 5, 13, 14, 15],
[ 6, 7, 8, 16, 17, 18]])
np.append([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], [[7, 8, 9]], axis=0)
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]])
Pandas merged
ser1 = pd.Series(['A', 'B', 'C'], index=[1, 2, 3])
ser2 = pd.Series(['D', 'E', 'F'], index=[4, 5, 6])
pd.concat([ser1, ser2])
1 A
2 B
3 C
4 D
5 E
6 F
df1 = make_df('AB', [1, 2])
df2 = make_df('AB', [3, 4])
display('df1', 'df2', 'pd.concat([df1, df2])')
Pandas Merge, join, and concatenate
Keras load model
try:
# load json and create model
json_file = open(save_dir+'model.json', 'r')
loaded_model_json = json_file.read()
json_file.close()
model = model_from_json(loaded_model_json)
# load weights into new model
model.load_weights(filename)
print("Loaded model from disk")
except :
PrintException()
model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer='adam', metrics=['mse'])
tensorflow log level turnoff
tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.ERROR)
ipython notebook module reload
import importlib
importlib.reload(pp)
How to deal with SettingWithCopyWarning in Pandas?
How to deal with SettingWithCopyWarning in Pandas?
df[df['A'] > 2]['B'] = new_val # new_val not set in df
df.loc[df['A'] > 2, 'B'] = new_val
df = df[df['A'] > 2]
df['B'] = new_val
pd.options.mode.chained_assignment = None # default='warn'
df.ix[:,'Score']
# Select 2nd row and 3rd column value
df.iloc[1,2]
# select 1st and 4thcolumn
df.iloc[:,[0,3]]
# select first 2 columns
df.iloc[:,:2]
df.loc[[1,2,3,4,5],['Name','Score']]
python reversed enumerate
for _fix,_val in reversed(list(enumerate(_holdlist))):
print(_fix,_val)
tensorflow memory config
config = tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True)
config.gpu_options.allocator_type = 'BFC'
config.gpu_options.per_process_gpu_memory_fraction = 0.40
config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
Multiple Models load
import glob
path = ''
dirnames=glob.glob(path)
model_len = len(dirnames)
models = []
for dirname in dirnames:
graph = tf.Graph()
sess = tf.Session(graph=graph)
with graph.as_default():
model = modelclass(sess,...)
model.load()
models.append(model)
File delete or remove in directory
files = glob.glob('./23/*')
for f in files:
os.remove(f)
os.rmdir(logs_dir)
Tensorflow save checkpoint option
# we don’t want to write the meta-graph we use this:
saver.save(sess, 'my-model', global_step=step,write_meta_graph=False)
# If you want to keep only 4 latest models and want to save one model after every 2 hours during training you can use max_to_keep and keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours like this.
saver = tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=4, keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours=2)
Shuffle Random
sentiment_data = pd.DataFrame()
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
sentiment_data = shuffle(sentiment_data)
Random Normal Generation
import scipy.stats as ss
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.arange(-10, 11)
xU, xL = x + 0.5, x - 0.5
prob = ss.norm.cdf(xU, scale = 3) - ss.norm.cdf(xL, scale = 3)
prob = prob / prob.sum() #normalize the probabilities so their sum is 1
nums = np.random.choice(x, size = 10000, p = prob)
plt.hist(nums, bins = len(x))
Cache Tutorial
from cache import cache
# If the cache-file already exists then reload it,
# otherwise process all images and save their transfer-values
# to the cache-file so it can be reloaded quickly.
transfer_values = cache(cache_path=cache_path,
fn=process_images,
data_dir=coco.train_dir,
filenames=filenames_train)
searching datetime index
1. index count finds the DateTimeIndex
dffault['index'] = np.arange(df_merged_test.shape[0])
tempdf = dffault['index'].iloc[int(startday):int(endday)].index
2. set the DateTimeIndex
dffault.ix[tempdf]
Using Dropout with Keras and LSTM/GRU cell
#In Keras you can specify a dropout layer like this:
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
#But with a GRU cell you can specify the dropout as a parameter in the constructor:
model.add(GRU(units=512,
return_sequences=True,
dropout=0.5,
input_shape=(None, features_size,)))
pandas floor
floored_data = data.apply(np.floor)
signal display
%matplotlib notebook
dftmp = augRLmergeddt[0][2]
dftmp[['Close']].plot()
buyindex = dftmp['signal_5ma'][dftmp['signal_5ma']==9].index
sellindex = dftmp['signal_5ma'][dftmp['signal_5ma']==-9].index
plt.scatter(buyindex,dftmp['Close'][buyindex],c='red')
plt.scatter(sellindex,dftmp['Close'][sellindex],c='green')
pandas week, month ,day
stocks_df['day'] = stocks_df['date'].dt.weekday
stocks_df['day_of_month'] = stocks_df['date'].dt.day
pandas dataframe column list extraction
list(norm_df)
>> ['close',
'close_avg_10',
'close_avg_3',
'close_avg_5',
'date',
'day',
'day_of_month',
'high',
'low',
'open']
sklearn LabelEncoder
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
le = LabelEncoder()
train = ["paris", "paris", "tokyo", "amsterdam"]
test = ["tokyo", "tokyo", "paris"]
print(le.fit(train).transform(test))
np.utils.to_categorical is used to convert array of labeled data(from 0 to nb_classes-1) to one-hot vector.
In [1]: from keras.utils import np_utils
Using Theano backend.
In [2]: np_utils.to_categorical?
Signature: np_utils.to_categorical(y, num_classes=None)
Docstring:
Convert class vector (integers from 0 to nb_classes) to binary class matrix, for use with categorical_crossentropy.
# Arguments
y: class vector to be converted into a matrix
nb_classes: total number of classes
# Returns
A binary matrix representation of the input.
File: /usr/local/lib/python3.5/dist-packages/keras/utils/np_utils.py
Type: function
In [3]: y_train = [1, 0, 3, 4, 5, 0, 2, 1]
In [4]: """ Assuming the labeled dataset has total six classes (0 to 5), y_train is the true label array """
In [5]: np_utils.to_categorical(y_train, num_classes=6)
Out[5]:
array([[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1.],
[ 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0.]])
sklearn train_test_split
You can use train_test_split twice. I think this is most straightforward.
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=1)
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(
X_train, y_train, test_size=0.25, random_state=1)
Keras Layer output merged -> How to concatenate two layers in keras?
from keras.models import Sequential, Model
from keras.layers import Concatenate, Dense, LSTM, Input, concatenate
from keras.optimizers import Adagrad
first_input = Input(shape=(2, ))
first_dense = Dense(1, )(first_input)
second_input = Input(shape=(2, ))
second_dense = Dense(1, )(second_input)
merge_one = concatenate([first_dense, second_dense])
third_input = Input(shape=(1, ))
merge_two = concatenate([merge_one, third_input])
model = Model(inputs=[first_input, second_input, third_input], outputs=merge_two)
model.compile(optimizer=ada_grad, loss='binary_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
# merge samples, two input must be same shape
inp1 = Input(shape=(10,32))
inp2 = Input(shape=(10,32))
cc1 = concatenate([inp1, inp2],axis=0) # Merge data must same row column
output = Dense(30, activation='relu')(cc1)
model = Model(inputs=[inp1, inp2], outputs=output)
model.summary()
# merge row must same column size
inp1 = Input(shape=(20,10))
inp2 = Input(shape=(32,10))
cc1 = concatenate([inp1, inp2],axis=1)
output = Dense(30, activation='relu')(cc1)
model = Model(inputs=[inp1, inp2], outputs=output)
model.summary()
# merge column must same row size
inp1 = Input(shape=(10,20))
inp2 = Input(shape=(10,32))
cc1 = concatenate([inp1, inp2],axis=1)
output = Dense(30, activation='relu')(cc1)
model = Model(inputs=[inp1, inp2], outputs=output)
model.summary()
Keras Lambda Layer Example
from keras.models import Model
#create dense layers and store their output tensors, they use the output of models 1 and to as input
d1 = Dense(64, ....)(Model_1.output)
d2 = Dense(64, ....)(Model_1.output)
d3 = Dense(64, ....)(Model_2.output)
d4 = Dense(64, ....)(Model_2.output)
cross1 = Lambda(myFunc, output_shape=....)([d1,d4])
cross2 = Lambda(myFunc, output_shape=....)([d2,d3])
#I don't really know what kind of "merge" you want, so I used concatenate, there are Add, Multiply and others....
output = Concatenate()([cross1,cross2])
#use the "axis" attribute of the concatenate layer to define better which axis will be doubled due to the concatenation
model = Model([Model_1.input,Model_2.input], output)
import keras.backend as K
def myFunc(x):
return x[0] * x[1]
pandas multi condition selection
df[(df['date'] > '2018-01-01') & (df['recon_error']> anomaly_threshold)].sort_values('recon_error', ascending=False)
matplotlib two axes in different scale
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots()
t = np.arange(0.01, 10.0, 0.01)
s1 = np.exp(t)
ax1.plot(t, s1, 'b-')
ax1.set_xlabel('time (s)')
# Make the y-axis label, ticks and tick labels match the line color.
ax1.set_ylabel('exp', color='b')
ax1.tick_params('y', colors='b')
ax2 = ax1.twinx()
s2 = np.sin(2 * np.pi * t)
ax2.plot(t, s2, 'r.')
ax2.set_ylabel('sin', color='r')
ax2.tick_params('y', colors='r')
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Fill in missing pandas data with previous non-missing value, grouped by key
df['x'] = df.groupby('id').fillna(method='ffill')
pandas merge
dfmerge = pd.merge(dfstock,dfval, left_index = True,right_index=True,how='left')
dfmerge = pd.merge(dfstock,dfval, left_index = True,right_index=True,how='inner')
dfmerge.fillna(method='bfill')
dfmerge.fillna(method='ffill')
pd.isna(df2['one'])
Python Pandas : How to add rows in a DataFrame using dataframe.append() loc[] iloc[]
remove brakets in pandas cell
portlogs = portlogs.append({'Date':curday,'Buy':buys,'Sell':sells},ignore_index=True)
# portlogs = portlogs.apply(lambda x: ",".join(x) if isinstance(x, list) else x)
portlogs['Buy'] = pd.DataFrame([str(line).strip('[').strip(']') for line in portlogs['Buy']])
portlogs['Sell'] = pd.DataFrame([str(line).strip('[').strip(']') for line in portlogs['Sell']])
class name, function name
클래스이름 = self.__class__.__name__
함수이름 = inspect.currentframe().f_code.co_name
get current directory
import os,sys
os.getcwd()
today searching datetimeindex, datetime
import datetime
today = datetime.date.today()
print(str(today))
dfstock.loc[str(today)]
dictionary append
from collections import defaultdict
d1 = {1: 2, 3: 4}
d2 = {1: 6, 3: 7}
dd = defaultdict(list)
for d in (d1, d2): # you can list as many input dicts as you want here
for key, value in d.iteritems():
dd[key].append(value)
print(dd)
Matplotlib pandas plot
mcdon['Adj. Close'].plot(xlim=['2007-01-01','2009-01-01'])
mcdon['Adj. Close'].plot(xlim=['2007-01-01','2009-01-01'],ylim=[0,50])
mcdon['Adj. Close'].plot(xlim=['2007-01-01','2007-05-01'],ylim=[0,40],ls='--',c='r')
idx = mcdon.loc['2007-01-01':'2007-05-01'].index
stock = mcdon.loc['2007-01-01':'2007-05-01']['Adj. Close']
# pandas datetime index to matplotlib x input
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.dates as dates
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot_date(idx, stock,'-')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot_date(idx, stock,'-')
ax.yaxis.grid(True)
ax.xaxis.grid(True)
fig.autofmt_xdate() # Auto fixes the overlap!
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot_date(idx, stock,'-')
# Grids
ax.yaxis.grid(True)
ax.xaxis.grid(True)
# Major Axis
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(dates.MonthLocator())
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(dates.DateFormatter('%b\n%Y'))
fig.autofmt_xdate() # Auto fixes the overlap!
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot_date(idx, stock,'-')
# Grids
ax.yaxis.grid(True)
ax.xaxis.grid(True)
# Major Axis
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(dates.MonthLocator())
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(dates.DateFormatter('\n\n\n\n%Y--%B'))
fig.autofmt_xdate() # Auto fixes the overlap!
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot_date(idx, stock,'-')
# Major Axis
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(dates.MonthLocator())
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(dates.DateFormatter('\n\n%Y--%B'))
# Minor Axis
ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(dates.WeekdayLocator())
ax.xaxis.set_minor_formatter(dates.DateFormatter('%d'))
# Grids
ax.yaxis.grid(True)
ax.xaxis.grid(True)
fig.autofmt_xdate() # Auto fixes the overlap!
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10,8))
ax.plot_date(idx, stock,'-')
# Major Axis
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(dates.WeekdayLocator(byweekday=1))
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(dates.DateFormatter('%B-%d-%a'))
# Grids
ax.yaxis.grid(True)
ax.xaxis.grid(True)
fig.autofmt_xdate() # Auto fixes the overlap!
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
pandas_datareader issue
import pandas as pd
pd.core.common.is_list_like = pd.api.types.is_list_like
import pandas_datareader
import datetime
pandas_datareader FRED
import pandas_datareader.data as web
import datetime
start = datetime.datetime(2010, 1, 1)
end = datetime.datetime(2017, 1, 1)
gdp = web.DataReader("GDP", "fred", start, end)
Numpy gzip save and load
np_train = outdfs['ECONET_INPUT_30'][0][0]
np_train.shape
import gzip
import numpy
f = gzip.GzipFile("./InputData/input_np_train.npy.gz", "w")
np.save(file=f, arr=np_train)
f.close()
with gzip.open("./InputData/input_np_train.npy.gz", 'r') as infile:
np_train_load= np.load(infile)
Assign new value in pandas
df.loc[df[<some_column_name>] == <condition>, [<another_column_name>]] = <value_to_add>
df_train['id'] = 0
df_train.loc[(df_train['signal_5ma'] == 9) | (df_train['signal_5ma'] == 8), ['id']] = 1
df_train.loc[(df_train['signal_5ma'] == -9) | (df_train['signal_5ma'] == 0), ['id']] = -1
numpy one hot encoding
id_PMLR = df_train['id'].values
print(id_PMLR.shape)
nb_classes = 2
targets = id_PMLR
one_hot_targets = np.eye(nb_classes)[targets]
one_hot_targets.shape
Keras one hot encoding
df_train = mergeddata[0][2]
df_train['id'] = 0
df_train.loc[(df_train['signal_5ma'] == 9) , ['id']] = 1
df_train.loc[(df_train['signal_5ma'] == 8) , ['id']] = 2
df_train.loc[(df_train['signal_5ma'] == -9) , ['id']] = 3
df_train.loc[(df_train['signal_5ma'] == 0) , ['id']] = 0
_val = df_train['id'].values
_val.shape
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler, OneHotEncoder
one_hot = OneHotEncoder() # one hot encode the target classes
np_target = one_hot.fit_transform(np.reshape(_val, (-1,1)) ).toarray()
Copy and add the last line of a python pandas data frame
df_data = df_data.append(pd.DataFrame(index=['2019-10-08'], data=df_data.tail(1).values, columns=df_data.columns))
Inserting row in pandas dataframe based on date using datetime index
col_A vi_B data_source index_as_date
2017-01-21 0.000000 0.199354 sat 2017-01-21
2017-01-22 0.000000 0.204250 NaN NaT
2017-01-23 0.000000 0.208077 NaN NaT
2017-01-27 0.000000 0.215081 NaN NaT
2017-01-28 0.000000 0.215300 NaN NaT
#if necessary convert to datetime
df.index = pd.to_datetime(df.index)
df['index_as_date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['index_as_date'])
df.loc[pd.to_datetime('2017-01-24')] = [0.01,0.4,'sat', pd.NaT]
df = df.sort_index()
print (df)
col_A vi_B data_source index_as_date
2017-01-21 0.00 0.199354 sat 2017-01-21
2017-01-22 0.00 0.204250 NaN NaT
2017-01-23 0.00 0.208077 NaN NaT
2017-01-24 0.01 0.400000 sat NaT
2017-01-27 0.00 0.215081 NaN NaT
2017-01-28 0.00 0.215300 NaN NaT
Inserting row in pandas dataframe based on date using datetime index